[lwptoc]
Our planet have been pushed to its limit by the economic model associated with the straight “take-make-dispose” model, unimaginable amount of wastes have been generated by this model, however, Circular Economy 2.0 have emerged and is taken center stage. This is not only about waste recycling, it is a fundamental shift towards regeneration – involves eliminating waste in the manufacturing process and restoring back to the natural system. Simply put “reducing harm to actively creating good.”
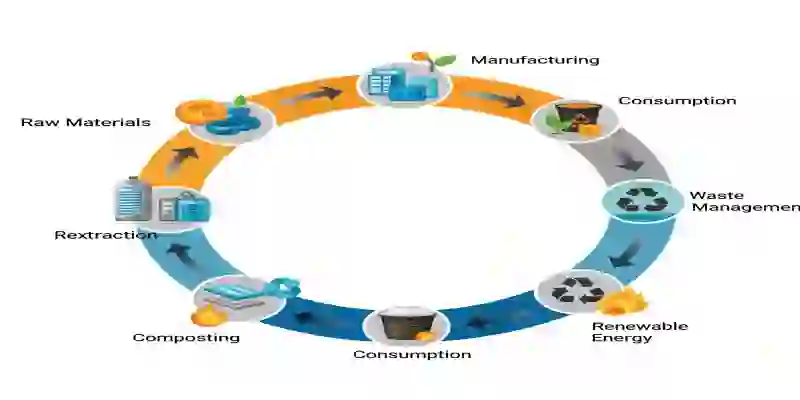
From Now to the Future: Our Future lies in Circularity
For many years, the world’s economies was built on one directional model of take (extract raw materials), make (manufacture products) and dispose them (when they are old). This one-way street kind of model leads to significant environmental impact leading to pollution and scarcity of resources. Circular Economy 2.0 emphasizes on the luminous model imagines a system where materials are kept in continues use throughout their lifecycles. The focus is to design a system that will remove wastes and pollution from the beginning of the process and enhances a regenerative model.
This process is crucial to economic survival and not just for the environment. When businesses engage in the principle of circularity they also add addition revenue streams, because now they do not budget for waste management as before and thus enhancing brand reputation – this is true because consumers are becoming more aware of the impact of their purchases on the environment and are thus seeking for product that reduces these bad impact and aligned with the regenerative values.
Fundamentals of Regeneration: Removing Waste
Below are the bedrock of Circular Economy 2.0 design rethinking proactive not reactive clean-up
- Product Design with Longevity and No/minimal Waste in Mind: this process takes into account the design of products that can last as long as possible – as made possible with product regeneration, product that can be easily replaced and upgraded, extending its lifecycle as against manufacturing new one.
- Material Knowledge and Traceability: When the components of a product are known it will be easy to implementing circularity, detailed ingredient of a product leads to traceability, origin and makes for informed decision for repairs, reuse and regeneration.
- Product Components with Renewability and Biodegradability: as the conversation shifts from linear to circularity, manufacturers and businesses should focus on making products with inputs that are degradable and renewable as this leads to waste reduction and pollution elimination.
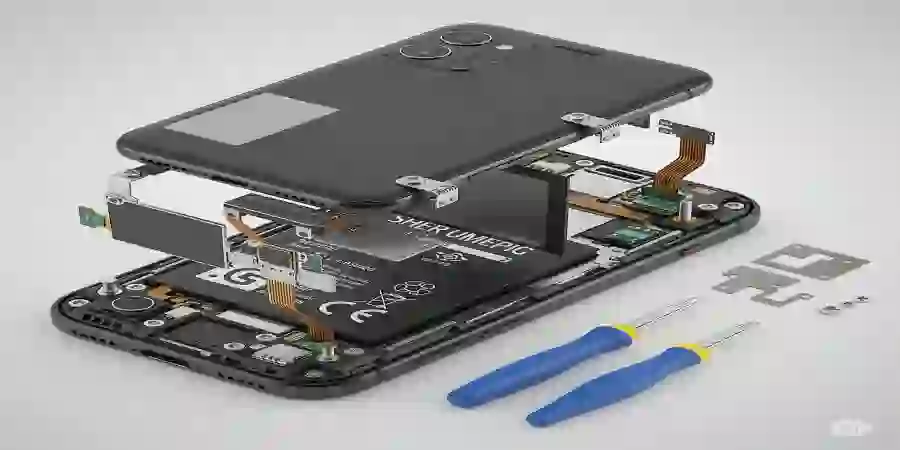

Imagining a smartphone with components easily replaceable or upgradable, thus extending its life and preventing e-waste.
Going Beyond the Products: Maintaining Circularity across the Value Chain
Circular Economy 2.0 goes way beyond the product itself and cuts across the different stages of value chain
- Sourcing Substantiality: buying mainly from suppliers with track record sustainable practices that does not impact the environment negatively, focusses on renewability, waste elimination and good ESG report. This is usually the first step in the implementation of circularity
- Efficient Production: Optimized manufacturing methods that minimizes water and energy consumption, using one waste for other manufacturing processes, this is a very good example of employing a regenerative
- Innovative Business Approaches:
- Remanufacturing and Repairs (RnR): When businesses are durable built it facilitates robust repair and remanufacturing practice – extending product life span as opposed to new manufacturing, can lead to the reduction in waist. Product as a Service (PaaS): Using the PaaS model entails offering rentals as against outright sales this makes it easy for manufacturer to aim at producing durable product, making them sole responsible for management, this will drastically reduce waste associated with individual management.
- Sharing options: Individual ownerships are usually associated with wastes but when platforms are shared, in enhances resource optimization
- Material Recovery and Reverse Logistics: Businesses should put in place and effective was or collecting and processing of used item, this encourages product recycling and fosters continuous regeneration.
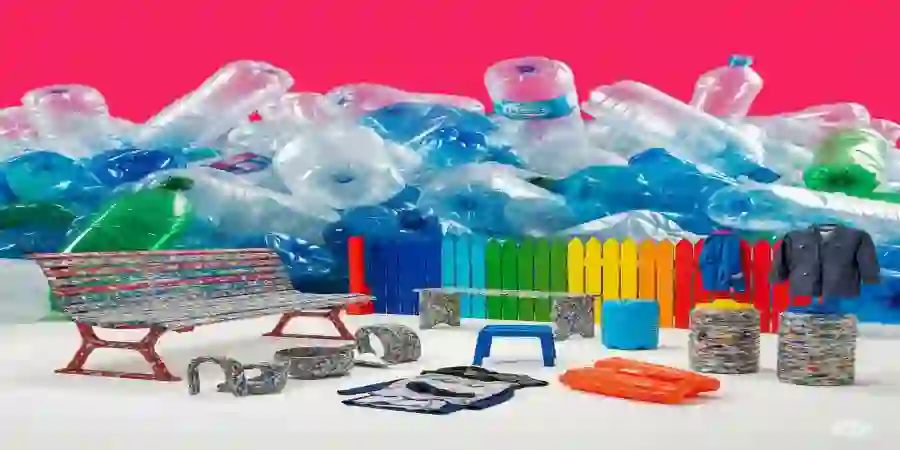

Regeneration from uselessness to usefulness : Waste plastic bottles being transformed into new products
Looking Ahead: Opportunities and Challenges for Circular Economy 2.0
While are inherent and enormous potentials associated with the circular economy 2.0, there still exist some obstacles that challenges its full realization. Overcoming the existing challenges – consumer behavior, regulatory framework and the existing framework that mostly favors the linear model requires
- Change in Consumer Behavior: Regular enlightenments about the benefits associated with a shift from the linear model a more preferred sustainable consumption that minimize waste.
- Aggressive Policy Support: Enabling policy enactment is very crucial encouraging circular practices and governments plays significant role in this regard – by developing effective and clear standards and enhancing collaborations across the different sectors can help in reducing wastes.
- Advancement in Technology: Increased research and investments in the remanufacturing, recycling and material management techniques, will help in unlocking new ways for regeneration.
To fully move into a fully regenerative economy that evidently eliminates wastes across the chains seems complex but at the same time exciting. It simply requires innovation, collaboration and deliberately rethinking of our production and consumption patterns. Embracing the Circular Economy 2.0 by businesses on the Global Impact Network, is all about utilizing the enormous opportunities for growth, positive impact and resilience that superbly needs regenerative future and not just risk mitigation. Let us come together to build a world where waste will be a thing of the past and regeneration a propelling principle for the future.









